The digital and creative sector is an important part of the economy, and creative jobs are embedded across numerous sectors, encompassing a wide range of activities, including: computer programming and consultancy; publishing; films, commercials and music; programming and broadcasting; video and audio recordings, games and publications, design and photography; and creative arts and entertainment.
The sector is a key providers of direct and indirect value – generating cross-over and spillover effects in terms of ideas, services, intellectual property and distinctiveness across the economy.
The media sector is experiencing an exciting period of change, with its focus continuing to shift to digital. Indeed, as digital becomes all pervasive there is an increased blurring of where one industry sector ends and another begins.
Spending on traditional paid media is coming under growing pressure as advertisers devote more resources to digital, database marketing, event marketing, place-based media and even loyalty programs.
As consumer time and spending are shifting to digital, there is increasing need to drive both innovation and efficiency, embracing new approaches to content development, distribution, operations, technology, and monetisation. In short, they need to adapt their strategies, capabilities, and operating models to address several key imperatives.
Traditional barriers associated with distribution and regulation, are no longer relevant, and emerging markets have become key to sustainable growth. Across Latin America, Asia, Russia and the Middle East, the multimedia landscape is developing rapidly. Companies looking for growth are evaluating partnerships and acquisitions that result in a greater exposure to these geographies.
The sector however presents some strategic opportunities.
To realise these, businesses needs to be more agile, adaptable and collaborative for sustainability and growth, which can then catalyse innovation and deliver value to other sectors through direct trade and spillover effects.
Further growth in demand for digital content and services, in particular, is expected to drive expansion of the digital and creative sector. There are particular concerns about the ability of the education system to supply the quantity and quality of workers needed for digital roles.
Reflecting the increasing convergence between digital and creative activities, technological trends will be the most important influence on the future development the digital and creative sector and its skills needs.
Significant technological trends will include: strong growth in demand for technology from across the economy; the growing importance of cyber security; the convergence of content across platforms; mobile and cloud computing; big data and analytics; the automation of routine tasks; new applications of social media; and new business models and collaborative platforms.
The future development of the sector could also be influenced by regulatory changes. Some of these may reflect the need to make current regulations more relevant to the digital world, such as changes to rules governing the ownership and use of data and intellectual property.
Demographic and economic factors will also shape skills needs. Workforces may increasingly include a more diverse mix of older workers that retire later, and millennials that bring a deep and intuitive knowledge of digital technologies.
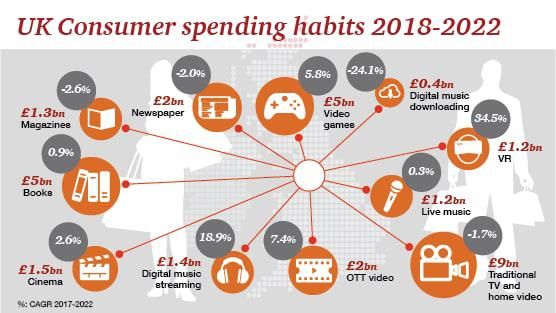
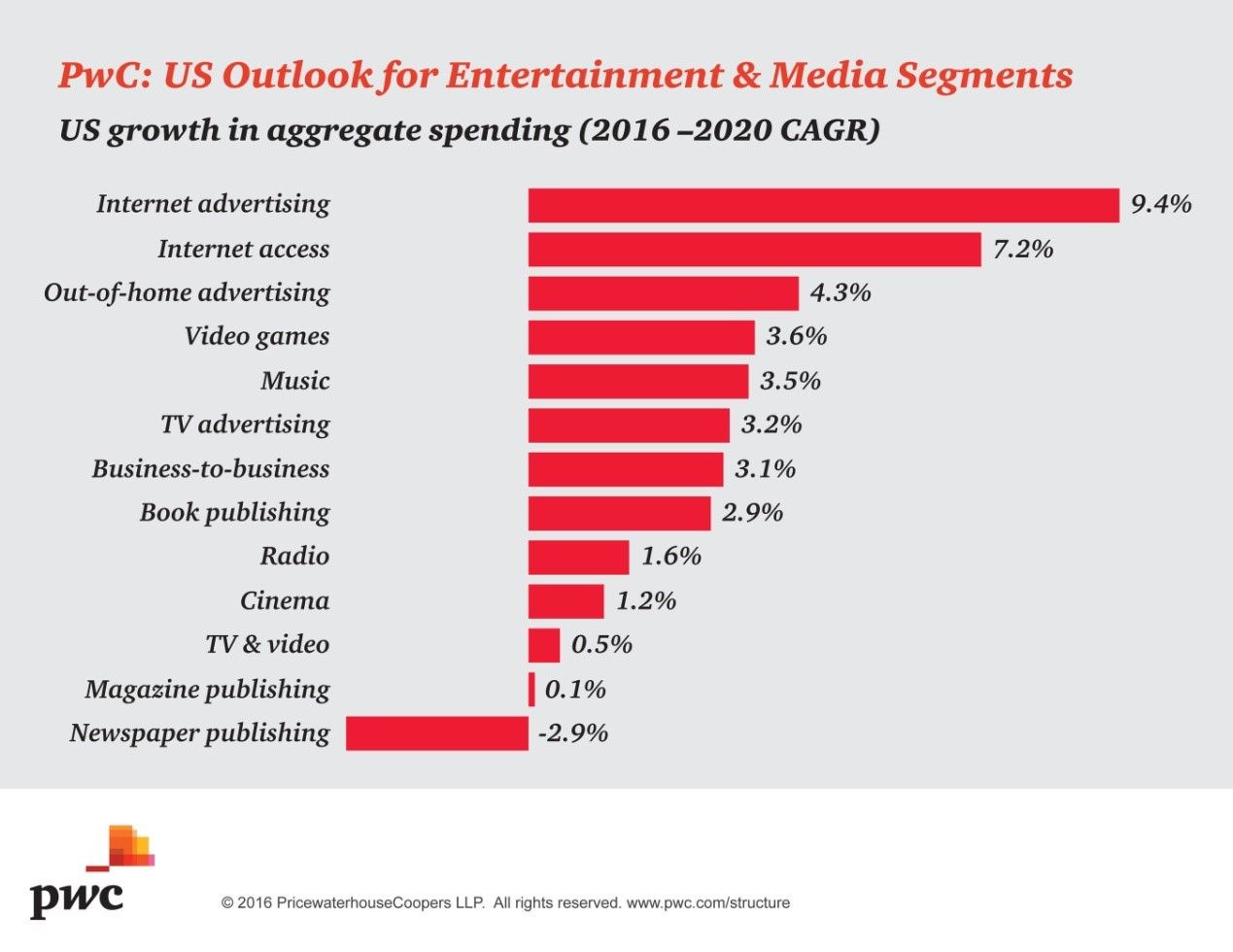
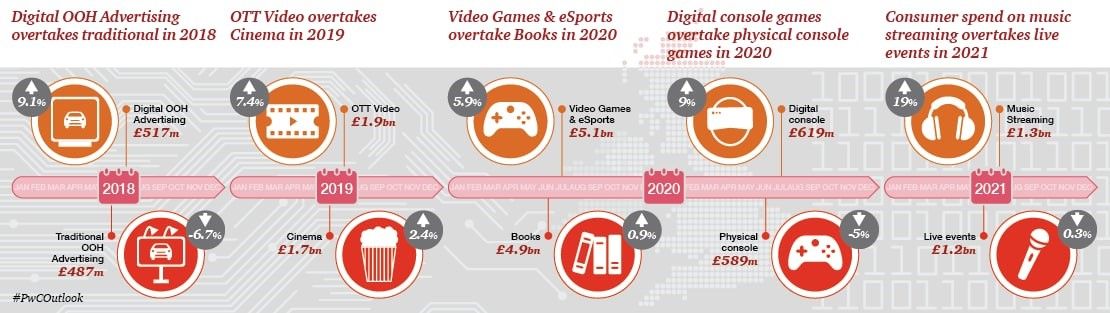
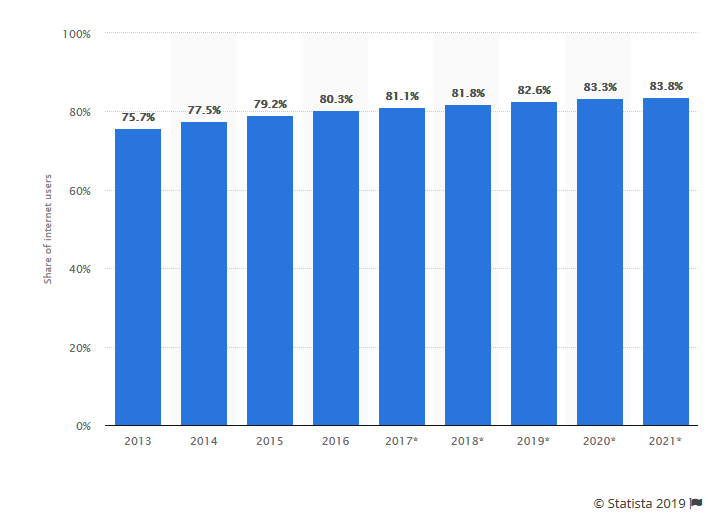
The shift to digital is bringing a transformation in the entertainment industry, as evidenced by increasing on demand viewership and consumer shifts toward web-based media and mobile apps.
In today’s search-driven world, as online video, social media and mobile media are expanding rapidly, consumers are actively looking for control, community, and interactivity. The goal for ad-relying media companies, is to move from creating impressions to building relationships with consumers. New relationship marketing strategies are in place to drive consumers to stores, theatres, and other screens as well as to activate other desirable actions.
Thus, every Media, Publishing & Entertainment company must gain a clear understanding of the legal environment in which it operates, and develop an effective voice for influencing the future course of that environment.



 Digital Media and Entertainment
Digital Media and Entertainment